Corrosion Under Insulation facilities

Overview
The Curtin Corrosion Centre developed corrosion under insulation (CUI) test facilities capable of evaluating insulation materials, determine the risk of CUI based on different environmental, operating conditions and materials of construction, as well as assessing coating and inhibitor performance under insulation.
Insulation materials can play significant roles in determining the risk of CUI. Therefore, understanding the behaviour of insulation materials is the first step in managing the risk of CUI. Fundamental properties relevant to corrosion that can be evaluated at the CCC include %water uptake and water retention, Leachable ion contents, and thermal ageing behaviour.
A unique test rig
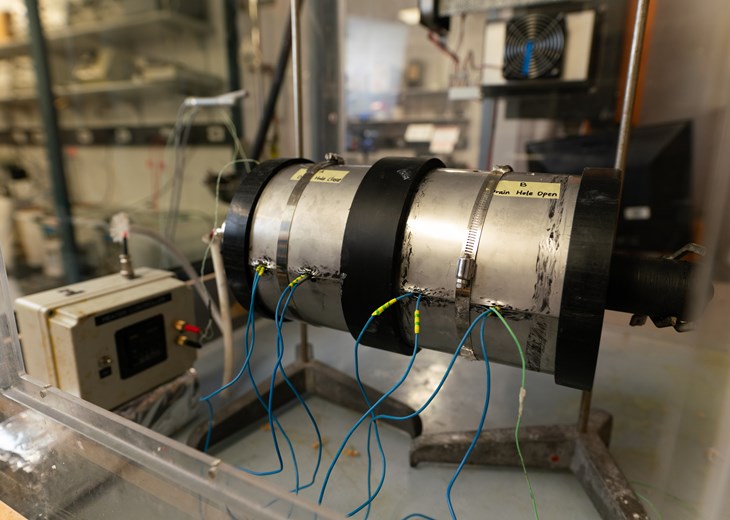
The Curtin Corrosion Centre designed and constructed a unique CUI test rig to evaluate CUI severity, CUI mechanisms, in situ monitoring, and the efficacy of chemical treatments and drain holes. The various CUI rigs can simulate hot service up to 150°C.
The apparatus can be placed in a custom chamber in which the relative humidity and temperature are controlled to mimic atmospheric conditions.
The normal fluctuations in weather conditions experienced in the field such as ambient temperature, %relative humidity can also be simulated and controlled by the environmental chamber. The chamber can be programmed to simulate the fluctuation in temperature and %RH during day and night time as well as seasonal profiles.
Advanced electrochemical monitoring & characterisation
The Curtin Corrosion Centre develops test protocols that allow in-situ insulation dry-out and corrosion monitoring using a combination of advanced electrochemical techniques such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and electrochemical noise (EN) methods.
CUI often manifests in localised corrosion form and complex corrosion product. Therefore, post-exposure analysis utilises a combination of techniques, including weight loss, 3D profilometry and the advanced microscopy facilities at the John de Laeter Centre, as well as corrosion product characterisation to provide valuable information concerning CUI risk.
Coatings under insulation
Protective coatings are regarded as the primary CUI barrier. Conditions under wet insulation can be severe not only from high temperature but also from constant water evaporation and condensing at the metallic substrates. Long-term coating performance can be evaluated at a constant temperature or using temperature cycling up to 150 °C. Post-exposure analyses take advantage of the various facilities at our disposal.
Typical experiments and conditions
Examples of CUI research conducted at the Curtin Corrosion Centre include the study of Insulation properties and CUI per relevant industry standards and tailored adaptations:
Insulation properties
- %water uptake and water retention,
- Leachable ion content (total anions and cations or selected ions Na+, SiO3, Cl, and F), and
- Thermal ageing at controlled temperatures.
Corrosion under insulation simulation
- Pipe temperature can be controlled from ambient up to 80°C or a temperature gradient can be applied up to 150°C.
- Environmental condition can be simulated to 25 to 35°C ambient temperature and 40 to 70 %RH.
- Isothermal or cyclic operating conditions
in-situ monitoring capabilities for insulation dry-out using EIS and localised corrosion initiation using EN technique. Ex-situ analysis includes weight loss, pit depth & morphology, corrosion product characterisation using SEM/EDS and XRD. - The test setup is suitable for various insulation materials.
Access to natural seawater for simulating water ingress at offshore conditions.



